Many people assume that all electronic devices should display the same colors, especially when they are from the same brand or model. In reality, this is not the case. If you place two identical monitors side by side and display the same image, there is at least a 95% chance that the colors will look different.
Why does this happen?
These differences can be noticed not only between monitors, but also among TVs, projectors, printers, and other devices. Even when the content is exactly the same, the visual result may vary. There are three main reasons for this:
1. Different Color Mixing Methods
There are two primary methods for producing color:
- Additive color mixing (RGB): used by monitors, LED/OLED displays, and projectors. Colors are generated by light. When red, green, and blue light combine, they produce white.
- Subtractive color mixing (CMY/CMYK): used in printing. Colors are created by pigment absorbing light on a surface such as paper. Combining cyan, magenta, and yellow produces, in theory, black.
Since the physical principles are different, the resulting colors cannot perfectly match between screens and printed materials.
2. Manufacturer Color Preferences
Each manufacturer calibrates its displays differently to achieve what they consider the best visual effect:
- Some enhance vividness
- Others focus on natural tones
- Others optimize brightness or contrast
Because of this, even two screens from the same brand may appear slightly different depending on the intended use (gaming, photography, video viewing, etc.).
3. Manufacturing Variations
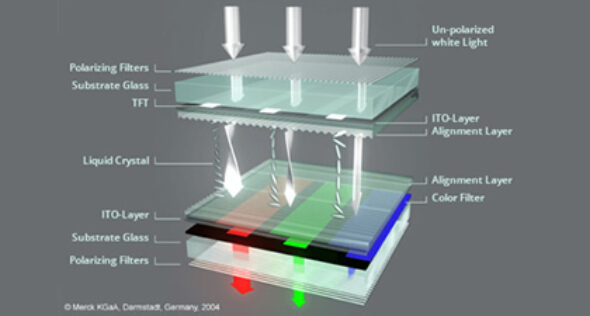
An LCD panel is made up of many layers (backlight, polarizers, liquid crystals, color filters, etc.).
Each layer can have a small production tolerance often around 2–5%.
When multiplied across 10+ layers, the final color variation can reach 15–20%.
Result: two new, seemingly identical monitors can still display different colors.
Conclusion
Color differences across devices occur for three main reasons:
- Different manufacturer calibration standards
- Differences between additive (screen) and subtractive (print) color mixing
- Component variations in mass production
In the next article, we will discuss how to calibrate devices to achieve the most consistent color appearance between screens, prints, and different display technologies.