Transparent OLED Displays: The Evolution of Digital Visualization
Technology evolves continuously, and few sectors illustrate this progress better than display technology. Among the most promising innovations are transparent OLED displays, a breakthrough poised to redefine how we interact with digital devices and our surroundings. This article explores the development and potential of transparent OLED displays, their applications across industries, the manufacturing challenges they present, and their projected market growth in the coming years.
What Transparent OLED Technology Is and How It Works
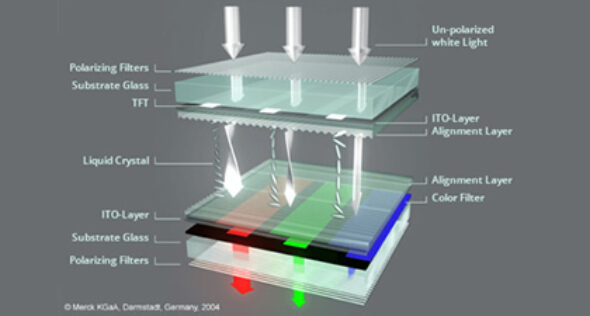
Transparent OLED displays are based on organic light-emitting diode (OLED) technology but are engineered to allow external light to pass through the screen. Thin layers of organic materials are deposited between two transparent electrodes, enabling the display to show digital content while remaining see-through when turned off. This feature makes them ideal for environments where digital elements must integrate seamlessly with real-world surroundings.
Main Advantages
- Transparency and lightness, allowing clear visibility through the screen without compromising image quality.
- High energy efficiency and superior contrast ratio.
- Wide viewing angles and accurate color reproduction.
- Capability to create flexible, foldable, or rollable displays, enabling advanced design applications.
Potential Applications
Transparent OLED displays have a wide range of uses across multiple industries:
- Retail: interactive shop windows displaying promotions or product information.
- Automotive: windshields and heads-up displays showing real-time data without obstructing visibility.
- Architecture: smart transparent surfaces for buildings and installations.
- Healthcare: transparent screens for diagnostic and surgical equipment.
- Consumer electronics: wearable devices and smart glasses with integrated digital interfaces.
The Manufacturing Process
Producing transparent OLED displays requires a high degree of precision:
1. Substrate preparation: glass or plastic is cleaned and treated.
2. Deposition of organic layers: performed through vacuum thermal evaporation to ensure layer uniformity and thickness control.
3. Encapsulation: protects organic materials from moisture and oxygen, extending the display’s lifespan.
The complexity of this process contributes to production costs, but ongoing research aims to optimize materials and techniques for broader commercial use.
Challenges and Solutions
- High production costs: due to expensive materials like indium tin oxide (ITO) and intricate manufacturing processes.
→ Solutions: developing alternative conductive materials and cost-efficient deposition methods. - Limited durability: organic compounds are sensitive to oxygen and humidity.
→ Solutions: advanced encapsulation techniques, thin-film barriers, and improved sealing methods. - Privacy and security issues: transparency may expose sensitive information.
→ Solutions: optical filters and smart visibility management systems.
Market Outlook
Market analysts forecast strong growth in the transparent OLED display market over the coming years, driven by:
- Increasing demand in retail, automotive, and architectural sectors;
- Technological and manufacturing advancements;
- Greater investment in research and development.
Although high production costs and technical limitations remain, the overall market outlook is positive, with significant expansion potential in the near future.
Conclusion
Transparent OLED technology marks a pivotal step forward in the evolution of display systems. Its combination of transparency, efficiency, and flexibility opens new frontiers for digital design and human–machine interaction, fundamentally changing how we experience visual interfaces. The future of display technology will be increasingly interactive, immersive, and seamlessly integrated into the real world and transparent OLED displays will be at the forefront of that transformation.