TOLED (Transparent Organic Light-Emitting Device) is an organic optoelectronic technology derived from OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) systems. It represents an evolution in the field of displays and lighting, offering thinner, lighter, and more energy-efficient solutions compared to traditional LED or LCD screens.
How TOLED Works
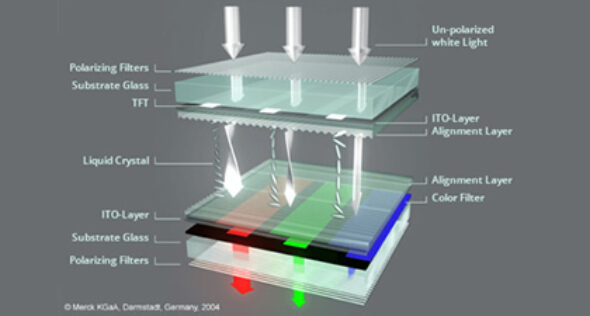
TOLED technology operates through the combination of two layers of organic materials: a thin organic semiconductor film and a transparent pair of anode and cathode electrodes. When voltage is applied, an electric current flows through the organic layers, which then emit visible light. This structure enables the creation of transparent screens that can allow external light to pass through while displaying bright and vivid images.
Applications of TOLED
TOLED technology can be used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Displays for smartphones, computers, and televisions;
- Thin, low-power lighting systems;
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices;
- Medical imaging equipment with transparent screens;
- Wearable devices and smart surfaces integrated into fabrics or objects.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Main advantages of TOLED:
- Ultra-thin and lightweight displays;
- High contrast and color accuracy;
- Improved energy efficiency;
- Longer lifespan compared to traditional LED or LCD technologies.
Main disadvantages:
- High production costs;
- Limited market availability;
- Need for improved material stability and durability over time.
TOLED Market Outlook
The TOLED market is expanding rapidly. Growing demand for lightweight, energy-efficient devices is driving projections that estimate a global market value of around USD 1.6 billion by 2026.
Companies and Manufacturers
Several major companies are investing in TOLED display and lighting development, including:
- Samsung, LG, Sony, and AU Optronics;
- Universal Display Corporation, which focuses on advanced materials and manufacturing processes.
Production methods include inkjet printing, vacuum deposition, and chemical vapor deposition, each offering specific benefits in precision and performance.
Types of TOLED
TOLED devices are generally divided into two categories:
- Small-molecule TOLEDs, made from low-molecular-weight organic compounds;
- Polymer TOLEDs, made from flexible polymer-based materials.
The two types differ in efficiency, durability, and production cost.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its advantages, TOLED technology still faces technical challenges related to material stability, light efficiency, and production costs. Current research focuses on developing new organic materials and fabrication techniques to enhance performance and reliability, paving the way for broader commercial adoption of TOLED displays in the near future.